Advanced Methods for Efficient PFAS Contamination Elimination
The relentless difficulty of PFAS contamination requires the expedition of advanced elimination approaches that can properly resolve these unsafe materials. Cutting-edge innovations, such as sophisticated oxidation processes and various adsorption techniques, have actually arised as appealing services in mitigating PFAS from impacted settings.
Recognizing PFAS Characteristics
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have actually been extensively used in different industrial and consumer items due to their special buildings, their determination in the atmosphere poses substantial obstacles to public health and safety and security. PFAS are a group of artificial chemicals characterized by a carbon-fluorine bond, among the best chemical bonds known, which adds to their extraordinary stability and resistance to destruction. This stability permits PFAS to collect in the environment and living microorganisms, causing possible unfavorable wellness impacts.
The hydrophobic and oleophobic nature of PFAS makes them particularly reliable in applications such as non-stick finishings, stain-resistant fabrics, and firefighting foams. These same buildings contribute to their ecological perseverance, as PFAS do not easily damage down via natural procedures. In addition, their widespread use has caused ubiquitous contamination of water sources and soils, complicating removal initiatives. Comprehending the chemical homes of PFAS is crucial for developing efficient approaches to manage and alleviate their ecological influence. The unique characteristics of these materials demand a nuanced approach to deal with the difficulties postured by their visibility in communities and prospective human exposure.
Ingenious Remediation Technologies
The persistence of PFAS in the atmosphere has spurred the development of innovative remediation modern technologies focused on properly eliminating these pollutants from impacted communities. Among one of the most encouraging techniques are advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), which make use of powerful oxidants to break down PFAS substances into less harmful materials. AOPs can be customized to target particular PFAS structures, improving their efficacy.
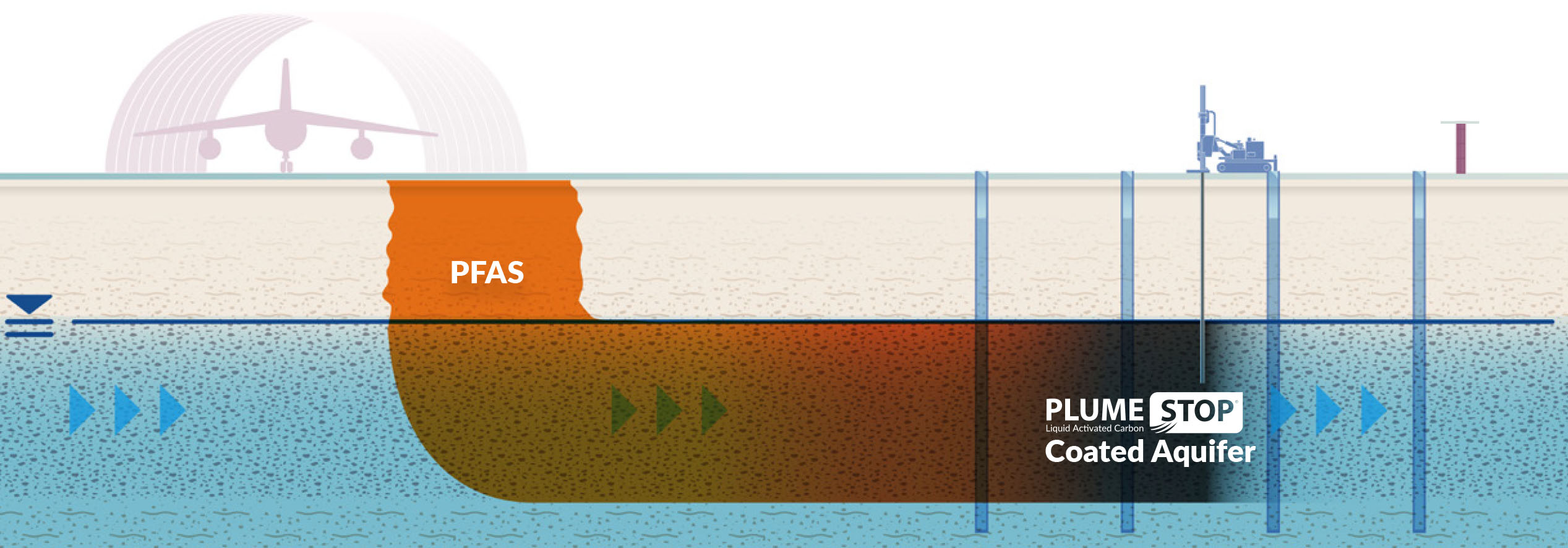
Another arising modern technology is making use of adsorption media, such as activated carbon and ion exchange materials, which can precisely capture PFAS from polluted water. These products have actually shown substantial removal efficiencies, although routine replacement and regrowth are needed to maintain efficiency.
Membrane purification methods, consisting of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are likewise gaining traction in PFAS removal. These techniques can effectively divide PFAS from water, providing a sensible service for dealing with polluted resources. Additionally, thermal therapy methods, such as incineration, can disintegrate PFAS into safe byproducts, though they need careful monitoring to manage exhausts.
Jointly, these innovative removal technologies represent significant advancements in the ongoing fight versus PFAS contamination, providing different strategies to bring back damaged atmospheres and protect public health and wellness.

Bioremediation Methods
Bioremediation techniques supply an appealing strategy to attending to PFAS contamination by taking advantage of the all-natural abilities of microorganisms to weaken these consistent compounds link (m270 waste management). This approach includes using microorganisms, fungi, and various other microbes that can metabolize or change PFAS substances right into less damaging results
Recent advancements in molecular biology and ecological microbiology have actually improved our understanding of microbial areas and their prospective functions in PFAS degradation. Scientists are proactively discovering details stress of bacteria, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have shown the ability to damage down particular PFAS compounds.
Sitting bioremediation strategies, where microorganisms are promoted straight in contaminated atmospheres, can be particularly effective. This method frequently includes the application of nutrients or electron benefactors to promote microbial growth and activity. Furthermore, ex-spouse situ methods, such as bioreactors, enable for regulated problems that can optimize degradation rates.
Regardless of the pledge of bioremediation, challenges stay, consisting of the intricate nature of PFAS substances and the need for substantial area screening - m270 waste management. Proceeded study and development will be vital to improve these strategies and analyze their effectiveness in diverse environmental contexts
Adsorption and Purification Methods
Dealing with PFAS contamination frequently includes utilizing adsorption and filtering techniques, which are developed to eliminate these persistent chemicals from water and soil. Among the various techniques, activated carbon adsorption is widely utilized due to its high surface area and porosity, enabling efficient capturing of PFAS particles. Granular turned on carbon (GAC) systems are particularly favored for dealing with huge quantities of contaminated water, while powdered turned on carbon (PAC) can be used for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange materials additionally show guarantee in PFAS removal, operating by exchanging PFAS ions with less hazardous ions in the water. This method has actually shown effectiveness in concentrating PFAS substances, promoting their subsequent removal. Additionally, membrane layer purification methods, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, operate by utilizing semi-permeable membrane layers to separate PFAS from water, effectively decreasing their concentrations.
While these approaches work, they should be thoroughly picked based on the specific PFAS substances present and the ecological context. Continuous advancements in products science and design are resulting in the development of unique adsorbents and filtration systems that enhance click resources elimination effectiveness and reduce functional costs, therefore enhancing overall removal efforts.
Regulatory and Plan Factors To Consider
How can reliable regulative structures enhance the administration of PFAS contamination? Comprehensive policies are important to make sure a worked with and durable action to the challenges presented by per- and polyfluoroalkyl materials (PFAS) Regulations can develop clear standards for monitoring, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated websites, cultivating accountability among markets and public entities. (m270 waste management)
Furthermore, economic incentives and grants can be incorporated right into policies to encourage the fostering of innovative removal technologies. Policymakers ought to additionally focus on r & d, making sure that arising approaches for PFAS removal are validated and carried out properly.
Moreover, public understanding and engagement are important components of any kind of regulative method, equipping areas to advocate for their health and wellness. Ultimately, a well-structured governing environment will not only enhance the management of PFAS contamination but additionally promote lasting methods that secure future generations.
Final Thought
In summary, the intricacy of PFAS contamination requires the fostering of sophisticated remediation methods. Proceeded research and growth in this field remain essential to attending to the challenges postured by PFAS contamination.